Diabetes Management with Nutrition Intervention
Diabetes is a medical condition that can cause one to become fatigued, feel extreme hunger, and experience other more serious problems over time. If one does not manage this disease, the person could develop more serious complications like vision problems, dementia, and kidney issues etc.
This article is about how one can improve one’s understanding of the evidence for a range of dietary approaches in diabetes, focusing on carbohydrate in diabetes, and to develop their personal strategies for supporting people with diabetes.
What is The Learning Outcome of This Article?
After reading this article the one will be able to:
- Describe the range of dietary approaches that can improve outcomes in diabetes
- Discuss the challenges in focusing on macronutrient proportions with regards to the diet for people with diabetes
- Demonstrate an understanding of the possible advantages and disadvantages of very low carbohydrate diets in diabetes
Why is Learning about Diabetes Management Important?
Diabetes management is crucial because diabetes is a chronic condition that requires ongoing attention and care.
People with diabetes have risk of complications that includes 2-3-fold increase in risk of CVD (heart attacks & strokes), nephropathy (kidney disease), neuropathy (nerve damage), retinopathy (eye damage). Also reduced Life expectancy and reduced Quality of Life.
Overall, diabetes management is essential for maintaining optimal health, preventing complications, and enhancing the overall well-being of individuals living with diabetes. It empowers individuals to lead fulfilling lives and reduces the risk of both short-term and long-term complications associated with the condition.
Nutrition Intervention Impact on Diabetes?
Nutrition interventions can have a significant impact on diabetes. Diet plays a crucial role in the management of diabetes, and making healthy food choices can help control blood sugar levels, prevent complications, and improve overall health. Here are some ways in which nutrition interventions can impact diabetes:
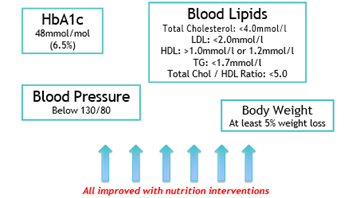
Hb1Ac
HbA1c, also known as glycated hemoglobin or hemoglobin A1c, is a laboratory test used to measure the average blood sugar levels over a period of approximately three months. It provides valuable information about a person’s long-term blood sugar control and is commonly used in the diagnosis and management of diabetes.
With dietary interventions Hb1Ac has been found to reduce.

Carbohydrate counting: Carbohydrate counting is a common nutrition intervention used in diabetes management. It involves estimating the amount of carbohydrates consumed in each meal and adjusting insulin doses accordingly. This approach helps individuals with diabetes maintain more stable blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Glycemic index/load: The glycemic index (GI) and glycemic load (GL) are measures that indicate how quickly a carbohydrate-containing food raises blood sugar levels. Nutrition interventions may focus on choosing foods with a lower GI and GL, as they cause a slower and more gradual rise in blood sugar. This approach can help individuals better control their blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications.
Macronutrient distribution: The balance of macronutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, in the diet can impact blood sugar control and overall health. Nutrition interventions may provide guidance on the appropriate distribution of macronutrients to optimize blood sugar management. For example, some individuals with diabetes may benefit from a higher protein or lower carbohydrate diet.
Fiber intake: Increasing dietary fiber intake, particularly from whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes, is often recommended in diabetes management. Fiber helps regulate blood sugar levels, improves insulin sensitivity, and promotes satiety, which also aids in weight management.
Blood Lipids and Blood Pressure: Heart health: People with diabetes have a higher risk of cardiovascular disease. Nutrition interventions often emphasize heart-healthy eating patterns, such as the Mediterranean diet or the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet. These diets focus on consuming nutrient-rich foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, while limiting processed foods, sugary beverages, and unhealthy fats.
Weight management – Body Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight is important for managing diabetes. Nutrition interventions focus on promoting a balanced diet that supports weight loss or weight maintenance, depending on the individual’s needs. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can improve insulin sensitivity, enhance blood sugar control, and reduce the risk of complications.
It is important to note that nutrition interventions should be personalized and tailored to an individual’s specific needs, taking into account factors such as age, weight, activity level, medications, and any other health conditions. Working with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional with expertise in diabetes management can help individuals develop a suitable nutrition plan that supports their overall health and blood sugar control.
Dietary Approaches
Dietary approaches refer to different methods or strategies for making food choices and structuring one’s eating habits to achieve specific health goals or address particular conditions. These approaches often involve guidelines and recommendations for nutrient intake, food selection, portion sizes, meal timing, and other factors related to nutrition. A Range of Dietary Approaches are adopted by people for diabetes management.
- Food based approaches:
- Mediterranean
- DASH
- Nordic Healthy Diet
- Nutrient focus approaches:
- High Fiber
- Low Glycemic Index
- Low Carbohydrate
- Very Low Carbohydrate
Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean Diet is a way of eating that is based on the traditional dietary patterns of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, such as Greece, Italy, Spain, and other Mediterranean countries. It is not just about the specific foods but also the overall dietary pattern and lifestyle. It encourages social interactions, regular physical activity, and emphasizes the enjoyment of meals with family and friends.
The main components of the Mediterranean Diet include:
High consumption of plant-based foods: The diet emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. These foods provide a wide range of vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber.
Olive oil as the primary source of fat: Olive oil is a key component of the Mediterranean Diet and is used as the primary source of fat in cooking and dressing salads. It is rich in monounsaturated fats and has been associated with various health benefits.
Moderate consumption of fish and poultry: Fish, especially fatty fish like salmon, sardines, and mackerel, is commonly consumed in the Mediterranean Diet due to its high omega-3 fatty acid content. Poultry is also consumed in moderate amounts, while red meat is limited.
Low to moderate consumption of dairy products: Dairy products like cheese and yogurt are included in moderation in the Mediterranean Diet. However, the consumption of full-fat dairy products is more common than low-fat options.
Limited consumption of red meat: Red meat, such as beef and pork, is limited in the Mediterranean Diet. It is typically consumed in small amounts and used more as a flavoring agent rather than the main protein source.
Moderate consumption of wine: Moderate consumption of red wine, usually during meals and in moderation, is a characteristic of the Mediterranean Diet. However, it’s important to note that excessive alcohol consumption is not recommended and individual tolerance may vary.
How is Mediterranean Diet beneficial for individuals with diabetes?
Improved blood sugar control: The Mediterranean Diet emphasizes whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables, which are rich in fiber and have a lower glycemic index. This means they are digested more slowly, leading to a slower rise in blood sugar levels after meals. The diet also includes healthy fats from sources like olive oil and nuts, which can help stabilize blood sugar levels.
Reduced risk of cardiovascular complications: People with diabetes have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. The Mediterranean Diet has been found to lower the risk of heart disease and stroke, which are common complications of diabetes. The consumption of monounsaturated fats, found in olive oil, as well as the inclusion of fatty fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, can help improve heart health.
Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight is important for managing diabetes. The Mediterranean Diet promotes a balanced and varied eating pattern that includes whole, unprocessed foods. It is not overly restrictive and can be sustainable in the long term, making it easier to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
Lower risk of insulin resistance: Insulin resistance is a condition in which the body’s cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. The Mediterranean Diet, with its focus on whole foods and healthy fats, has been associated with a lower risk of insulin resistance.
Anti-inflammatory effects: Chronic inflammation is believed to play a role in the development and progression of diabetes. The Mediterranean Diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fatty fish, which contain anti-inflammatory compounds such as antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids. These components can help reduce inflammation in the body.
DASH Diet
The DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet is a dietary pattern specifically designed to help lower blood pressure but it also helps people having diabetes.
The key features of the DASH diet include:
High consumption of fruits and vegetables: The DASH diet encourages eating a variety of fruits and vegetables, which are excellent sources of vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. They are low in sodium and high in potassium, which can help lower blood pressure.
Emphasis on whole grains: The DASH diet promotes whole grains like whole wheat, brown rice, oats, and quinoa. These grains provide more nutrients and fiber compared to refined grains.
Inclusion of low-fat dairy products: The diet includes low-fat or fat-free dairy products such as milk, yogurt, and cheese. These foods are rich in calcium, potassium, and magnesium, which are beneficial for blood pressure control.
Moderate consumption of lean proteins: The DASH diet recommends consuming moderate amounts of lean protein sources like poultry, fish, and legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas). These protein sources are low in saturated fat and provide important nutrients.
Limited intake of saturated and trans fats: The DASH diet advises limiting the intake of saturated fats, found in red meat, butter, and full-fat dairy products. It also emphasizes avoiding trans fats, which are found in many processed and fried foods.
Reduction of sodium intake: The DASH diet recommends reducing sodium intake to help lower blood pressure. It suggests limiting high-sodium foods, such as processed foods, canned soups, and salty snacks. Instead, herbs, spices, and salt substitutes can be used to flavor meals.
Moderate consumption of sweets and sugary beverages: The DASH diet suggests limiting the intake of sweets and sugar-sweetened beverages, as they provide empty calories and can contribute to weight gain and other health issues.
How is DASH Diet beneficial for individuals with diabetes?
The DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet is also beneficial for individuals with diabetes. While it was initially developed to lower blood pressure, its emphasis on whole foods, nutrient-rich choices, and balanced eating can contribute to better diabetes management. Here’s how the DASH diet can help in diabetes management:
Blood sugar control: The DASH diet promotes a balanced intake of carbohydrates from whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. These foods have a lower glycemic index, meaning they are digested more slowly and result in a slower rise in blood sugar levels. The emphasis on whole grains and fiber-rich foods can help stabilize blood sugar levels and improve glycemic control.
Weight management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is essential for diabetes management. The DASH diet encourages the consumption of nutrient-dense, low-calorie foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, which can help with weight management and improve insulin sensitivity.
Heart health: Individuals with diabetes have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. The DASH diet has been shown to reduce the risk of heart disease by promoting the consumption of fruits, vegetables, low-fat dairy products, and lean proteins. By supporting heart health, the DASH diet can have additional benefits for individuals with diabetes.
Reduced sodium intake: The DASH diet encourages limiting sodium intake, which is also beneficial for individuals with diabetes. High sodium intake can contribute to high blood pressure and increase the risk of cardiovascular complications. By reducing sodium intake and focusing on whole foods instead of processed ones, the DASH diet supports overall cardiovascular health.
Improved lipid profile: The DASH diet is associated with improvements in lipid profiles, including reduced levels of total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and triglycerides. This can be beneficial for individuals with diabetes who often have abnormal lipid levels and an increased risk of cardiovascular problems.
Overall healthy eating pattern: The DASH diet promotes a balanced and nutrient-rich eating pattern that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products. This encourages a well-rounded intake of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which can support overall health and diabetes management.
Nordic Healthy Diet
The Nordic Healthy Diet, also known as the New Nordic Diet, is a dietary pattern that focuses on the traditional foods and eating habits of the Nordic countries, including Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden. It was developed by nutritionists, chefs, and scientists with the aim of promoting health, sustainability, and cultural heritage. The main principles of the Nordic Healthy Diet include:
High consumption of fruits and vegetables: The diet emphasizes the intake of a variety of seasonal fruits and vegetables, including berries, root vegetables, leafy greens, and cruciferous vegetables. These foods are rich in vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants.
Emphasis on whole grains: Whole grain products like rye bread, oats, barley, and whole grain cereals are central to the Nordic Healthy Diet. They provide complex carbohydrates, fiber, and important nutrients.
Inclusion of fatty fish: Fatty fish such as salmon, herring, mackerel, and trout are commonly consumed in the Nordic Healthy Diet. These fish are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health and have anti-inflammatory properties.
Moderate consumption of lean meats and poultry: Lean meats and poultry, such as game meats and chicken, are consumed in moderation. The emphasis is on choosing high-quality, sustainably sourced options.
Use of rapeseed oil: Rapeseed oil (also known as canola oil) is a commonly used cooking oil in the Nordic Healthy Diet. It is low in saturated fat and rich in monounsaturated fats and omega-3 fatty acids.
Limited intake of processed foods: The Nordic Healthy Diet emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods and discourages the consumption of processed foods, sugary snacks, and beverages.
Focus on local, seasonal, and sustainable ingredients: The diet promotes the use of locally sourced and seasonal ingredients, supporting sustainability and reducing the carbon footprint associated with food production and transportation.
How is Nordic Healthy Diet beneficial for individuals with diabetes?
The Nordic Healthy Diet is helpful in managing diabetes due to several reasons:
Balanced carbohydrate intake: The Nordic Healthy Diet emphasizes whole grains, such as rye bread, oats, and barley, which have a lower glycemic index compared to refined grains. This means they are digested more slowly, resulting in a slower rise in blood sugar levels. The diet also includes a variety of fruits and vegetables, which provide important nutrients and fiber while contributing to a balanced carbohydrate intake.
High in fiber: The Nordic Healthy Diet is rich in dietary fiber due to the emphasis on whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes. Fiber helps regulate blood sugar levels by slowing down the absorption of glucose, improving glycemic control, and promoting satiety.
Consumption of fatty fish: Fatty fish, such as salmon, herring, and mackerel, are a prominent part of the Nordic Healthy Diet. These fish are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have been associated with improved insulin sensitivity and reduced risk of cardiovascular complications in individuals with diabetes.
Use of rapeseed oil: Rapeseed oil, commonly used in the Nordic Healthy Diet, is low in saturated fat and high in monounsaturated fats. These healthier fats can help improve blood lipid profiles and reduce the risk of heart disease, which is of particular importance for individuals with diabetes who have an increased risk of cardiovascular complications.
Emphasis on whole, unprocessed foods: The Nordic Healthy Diet focuses on consuming whole, unprocessed foods, which are generally lower in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium. By reducing the intake of processed foods and emphasizing whole foods, the diet supports a healthier overall eating pattern and can help with blood sugar control.
Weight management: The Nordic Healthy Diet, with its emphasis on nutrient-dense, fiber-rich foods and balanced meals, can support weight management efforts. Maintaining a healthy weight is important for individuals with diabetes as it can help improve insulin sensitivity and glycemic control.
Sustainable lifestyle: The Nordic Healthy Diet promotes a sustainable approach to food choices, including the use of locally sourced and seasonal ingredients. This focus on sustainable practices aligns with an overall healthy and environmentally conscious lifestyle, which can have positive impacts on overall well-being.
High Fiber
A high-fiber diet is helpful in managing diabetes. Here are several reasons why a high-fiber diet can benefit individuals with diabetes:
Improved blood sugar control: Dietary fiber, particularly soluble fiber, can slow down the absorption of glucose in the digestive system, resulting in a more gradual and steady rise in blood sugar levels after meals. This can help improve glycemic control and prevent spikes in blood sugar levels. It also contributes to better insulin sensitivity.
Increased satiety: High-fiber foods tend to be more filling and can help increase satiety, leading to reduced hunger and better appetite control. This can be beneficial for managing weight and preventing overeating, which is important for individuals with diabetes, as excess weight can negatively impact blood sugar control.
Enhanced weight management: A high-fiber diet can support weight management efforts. Fiber-rich foods generally have fewer calories for their volume, and they require more chewing and take longer to eat, promoting a feeling of fullness. By including plenty of fiber in your diet, you may naturally consume fewer calories, which can help with weight loss or weight maintenance.
Reduced risk of cardiovascular disease: Individuals with diabetes have an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease. A high-fiber diet, particularly one rich in soluble fiber, has been associated with improved lipid profiles, including reduced levels of total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and triglycerides. These improvements can contribute to better cardiovascular health.
Better digestive health: Fiber promotes regular bowel movements and helps prevent constipation. It can also contribute to a healthy gut microbiome by providing nourishment for beneficial gut bacteria. Good digestive health is important for overall well-being and can support nutrient absorption.
It’s important to note that when increasing fiber intake, it should be done gradually and accompanied by adequate hydration to prevent digestive discomfort.
Low Glycemic Index
A low glycemic index (GI) diet can be helpful in managing diabetes. The glycemic index is a scale that ranks carbohydrate-containing foods based on how much they raise blood sugar levels compared to a reference food, typically pure glucose. Foods with a low GI value have a smaller impact on blood sugar levels, while those with a high GI value cause a more rapid and pronounced increase.
It benefits individuals with diabetes in the following ways:
Improved blood sugar control: Foods with a low GI value are digested more slowly, resulting in a slower and more gradual rise in blood sugar levels. By choosing carbohydrates that have a lower impact on blood sugar, individuals with diabetes can achieve better glycemic control and reduce the risk of spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels.
Enhanced insulin sensitivity: A low GI diet has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, which means that the body’s cells become more responsive to the effects of insulin. This can help improve the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels and reduce insulin resistance, a key factor in type 2 diabetes.
Increased satiety and weight management: Low GI foods tend to be more filling and can help increase satiety, which can be beneficial for managing weight. By promoting feelings of fullness and reducing hunger, a low GI diet can support weight loss or weight maintenance efforts. Maintaining a healthy weight is important for individuals with diabetes, as excess weight can negatively impact blood sugar control.
Reduced risk of cardiovascular disease: Individuals with diabetes have an increased risk of cardiovascular complications. A low GI diet, which typically includes more whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes, has been associated with a reduced risk of heart disease and improved lipid profiles, including lower levels of total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol.
Balanced energy levels: Foods with a lower GI value provide a more sustained release of energy. By choosing low GI carbohydrates, individuals with diabetes can avoid the rapid rise and subsequent crash in blood sugar levels, helping to maintain more consistent energy levels throughout the day.
It’s important to note that while the glycemic index can be a useful tool, it has some limitations. The GI value of a food can be influenced by several factors, including the ripeness of the food, the cooking method, and the presence of other macronutrients in the meal. Additionally, individual responses to specific foods can vary. Therefore, it’s recommended to consider the overall quality of the diet, including a balance of nutrients and portion sizes, rather than solely focusing on GI values.
Low Carbohydrate
A low carbohydrate diet can be helpful in managing diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes. Here’s how a low carbohydrate diet can benefit individuals with diabetes:
Improved blood sugar control: Carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood sugar levels, as they are broken down into glucose during digestion. By reducing carbohydrate intake, individuals with diabetes can lower their blood sugar levels and improve glycemic control. Consuming fewer carbohydrates means there is less glucose available to raise blood sugar levels, which can be particularly beneficial for individuals with insulin resistance or difficulty in regulating blood sugar levels.
Reduced need for medication: Adopting a low carbohydrate diet can lead to decreased reliance on diabetes medications, including insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents. As blood sugar levels stabilize with lower carbohydrate intake, medication dosages may need to be adjusted under medical supervision to prevent hypoglycemia.
Weight management: Low carbohydrate diets often lead to weight loss, which is beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes, as excess weight can contribute to insulin resistance and difficulty in managing blood sugar levels. By reducing carbohydrate intake, the body is prompted to burn stored fat for energy, resulting in weight loss. Additionally, low carbohydrate diets tend to promote feelings of satiety, potentially reducing overall calorie intake.
Improved lipid profile: Low carbohydrate diets have been shown to improve lipid profiles by reducing triglyceride levels and increasing levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, often referred to as “good” cholesterol. This can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications, which is important for individuals with diabetes who are at an increased risk of heart disease.
Better insulin sensitivity: Restricting carbohydrate intake can enhance insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to utilize insulin more effectively. This can improve the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the insulin resistance commonly observed in type 2 diabetes.
It’s important to note that the effectiveness of a low carbohydrate diet may vary among individuals, and not all individuals with diabetes may benefit from or require a strictly low carbohydrate approach. The dietary needs and preferences of individuals can differ, and it’s essential to consider other factors such as overall nutritional balance, individual tolerance to carbohydrates, and personal health goals.
Conclusion
Based on above information we reach the conclusion that for diabetes management:
- Weight loss remains a key priority (>5%)
- Remission may be possible
- Evidence lacking for specific balance of macros, but
- Low CHO (50-130g/day) effective up to 6-12months for HbA1c & weight
- Promote food-based messages (rather than nutrients):
- Mediterranean / DASH / Nordic
- Several approaches are effective:
- Tailor approach to the individual
With any dietary plan, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to tailor the diet to your specific needs and make any necessary adjustments based on your health conditions and personal preferences.
Please contact me Abhinav Malhotra to learn what I and my team AbhiFit can do for you through personal training and nutrition services. We train kids, teens, adults, elders, athletes and models in Dubai and online across the UAE and around the world. We help our clients achieve their fat loss, weight loss, muscle gain, strength gain, rehab, figure / physique transformation & healthy living goals.
Many female and male clients including kids, teens, adults and elderly people have greatly benefited from Abhinav’s strong experience as the best personal trainer and nutritionist in Dubai, UAE. You can see some of our client transformations here here.
Email your Name and WhatsApp No. to info@abhifit.com if you want to receive a notification whenever we publish a new article.
Get Fit Now!
References


About Author
Abhinav Malhotra
Abhinav Malhotra is an award-winning personal trainer, coach and sports nutritionist in Dubai, UAE. He also offers online services to clients around the world. A personal trainer par excellence, Abhi has worked with the world’s leading fitness chains, supplement brands and founded his own fitness academy in India. He has achieved successes for many clients from all backgrounds and has trained the Indian Army Rugby Team. He is the first International Kettlebell Sport athlete from India.